Thyroid Plus Package
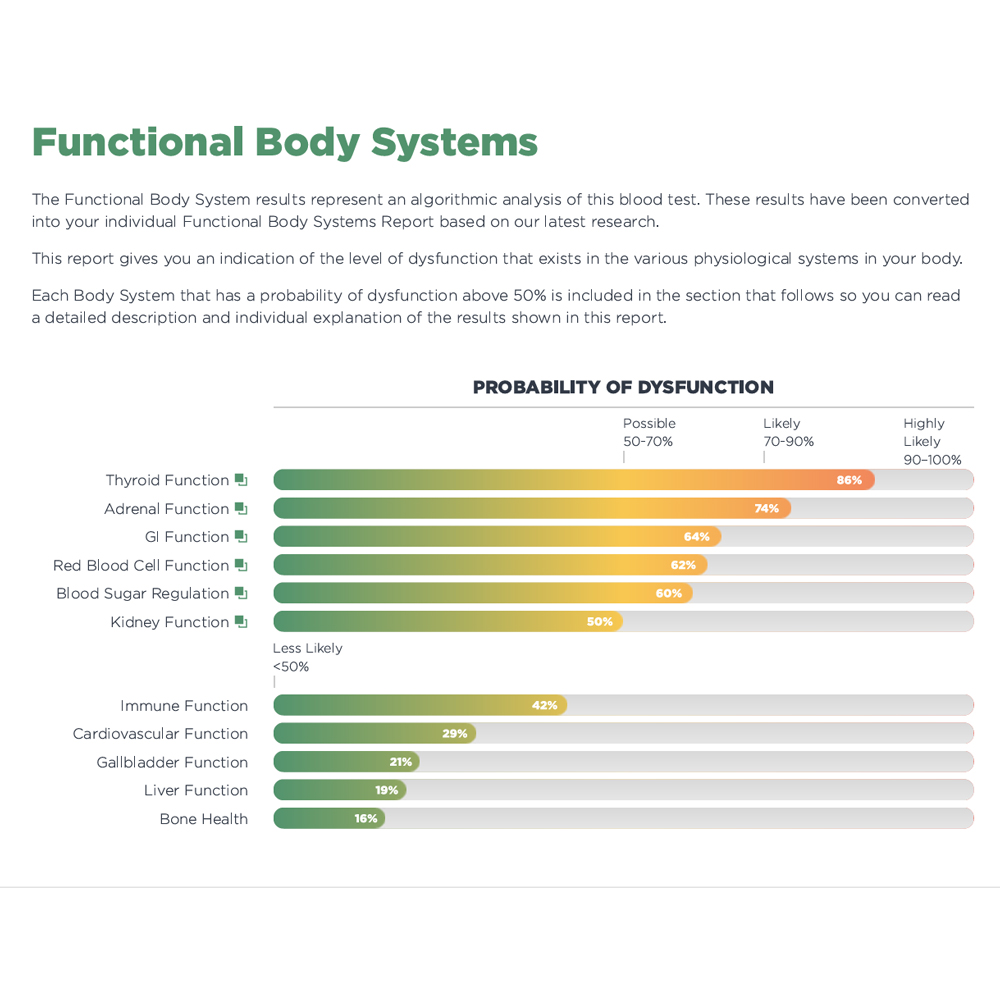
This is the ideal package for individuals looking for a deep understanding of their test results and a plan of action to change their health. This package includes everything in the Thyroid Standard Package plus much, much more! It includes the Functional Blood Test Health Report, 60-minute phone consultation with Dr. Sexton, supplement recommendations based on your test results and more.
The Thyroid Plus Package includes:
- Comprehensive 70+ test thyroid and metabolism panel (see full list of tests below)
- Test results as provided by Labcorp
- Functional Blood Test Health Report with detailed insights about your lab results
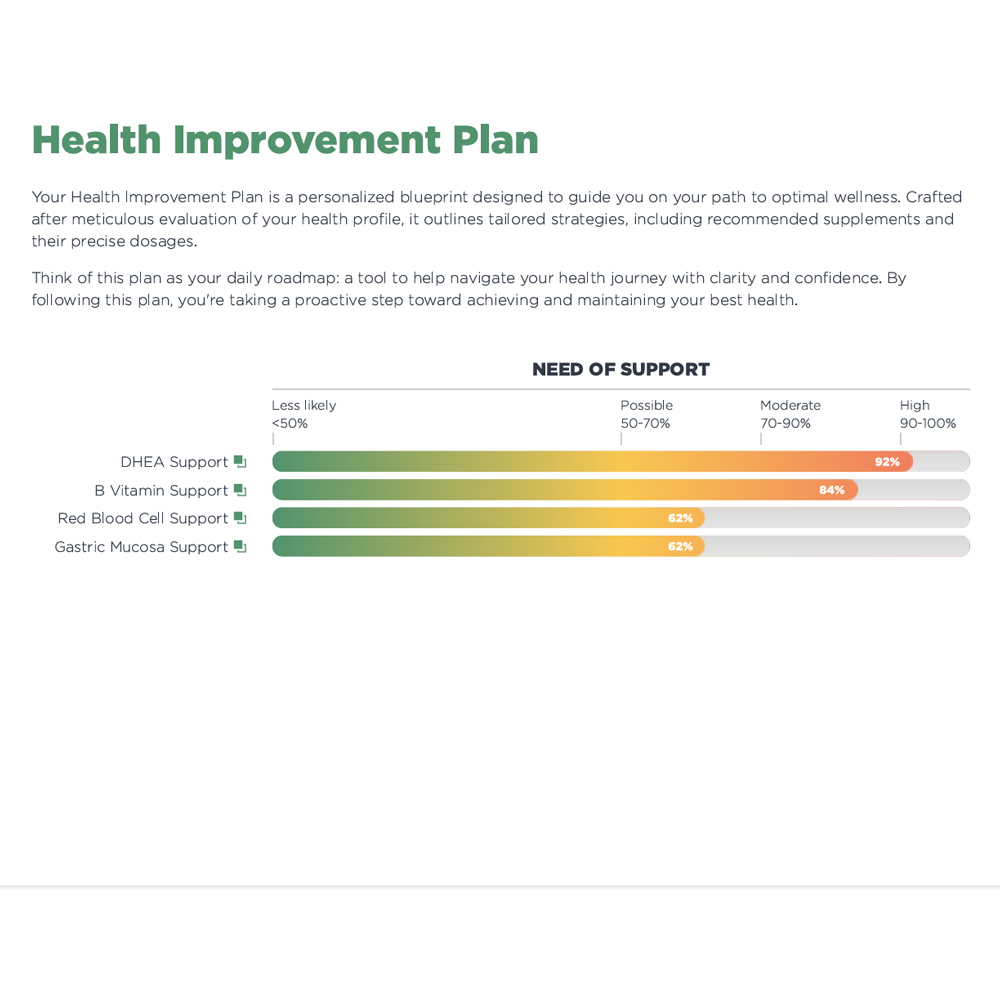
- Dietary Supplement suggestions based on your blood test results from Dr. Sexton
- Food plan based on your test results for optimum thyroid and metabolic function
- 20% off professional-grade dietary supplements through Fullscript
- 60-minute phone consultation with Dr. Sexton to review your results and answer any questions you have about your testing
$867.00
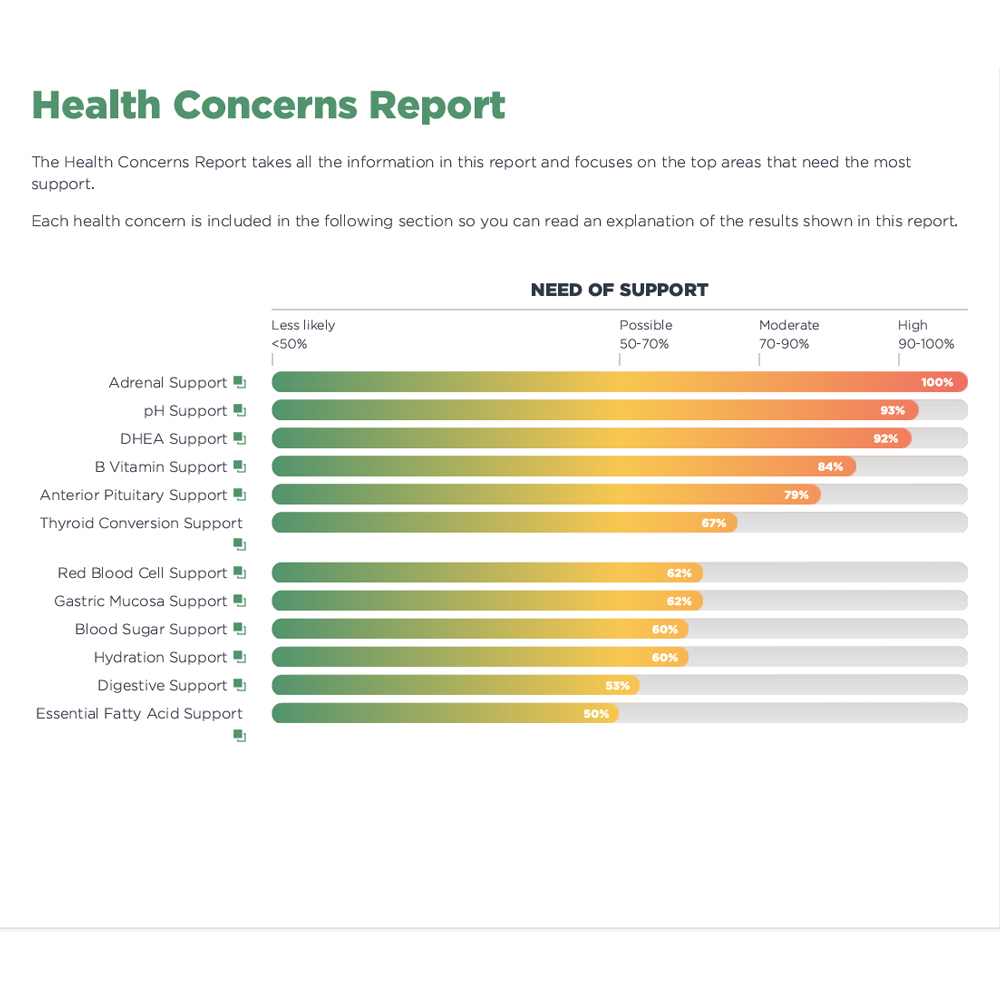
The Thyroid Plus Package helps provide the information you need to make informed decisions about your health and wellbeing.
The Thyroid Plus Package is designed for individuals who want to find out what is out of balance with their body using professional testing, get much more insight into what their test results mean as well as dietary supplement suggestions based on your test results and a food plan to help optimize thyroid health and metabolism.
Stop guessing and get real answers…only testing can do this for you.
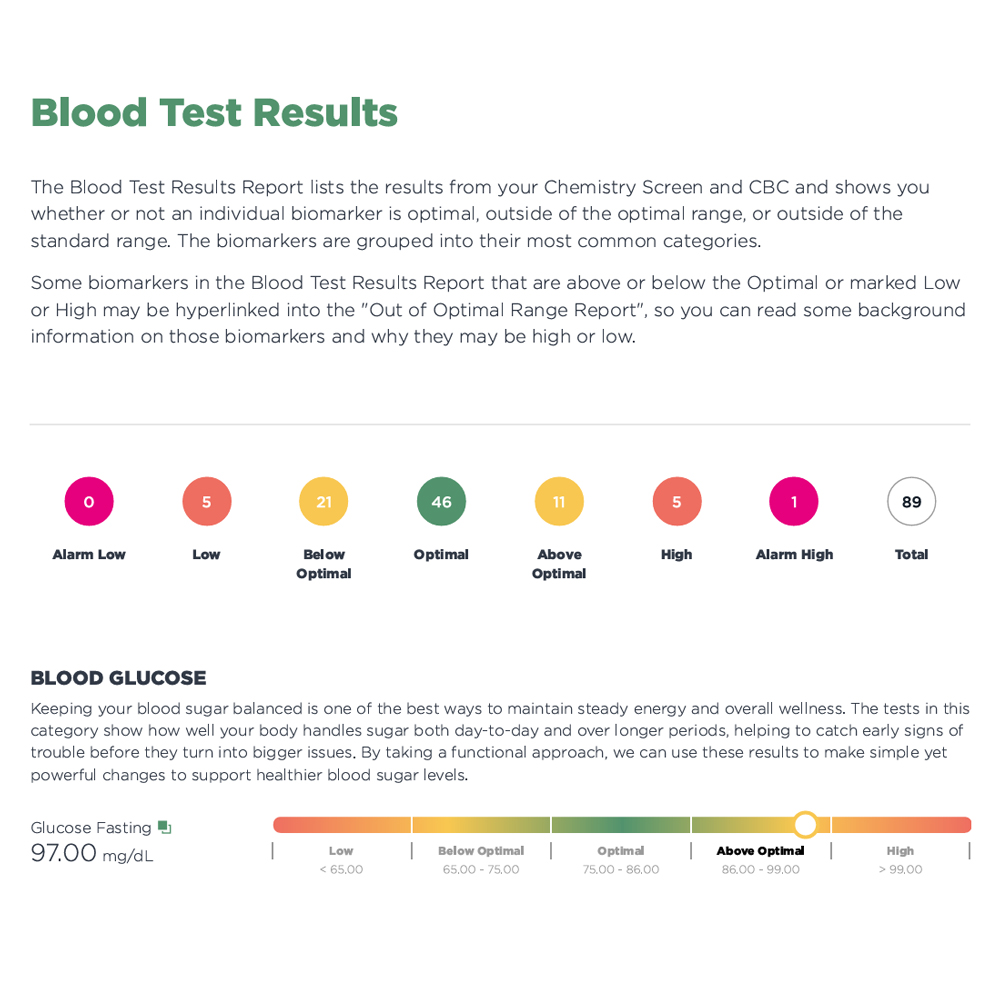
Dr. Sexton’s 70+ Thyroid and Metabolism Blood Test
The Thyroid and Metabolism panel includes 72 tests for women and 71 tests for men.
Female tests include estradiol, progesterone and testosterone.
Male tests do not include estradiol or progesterone but do include testosterone and free testosterone.
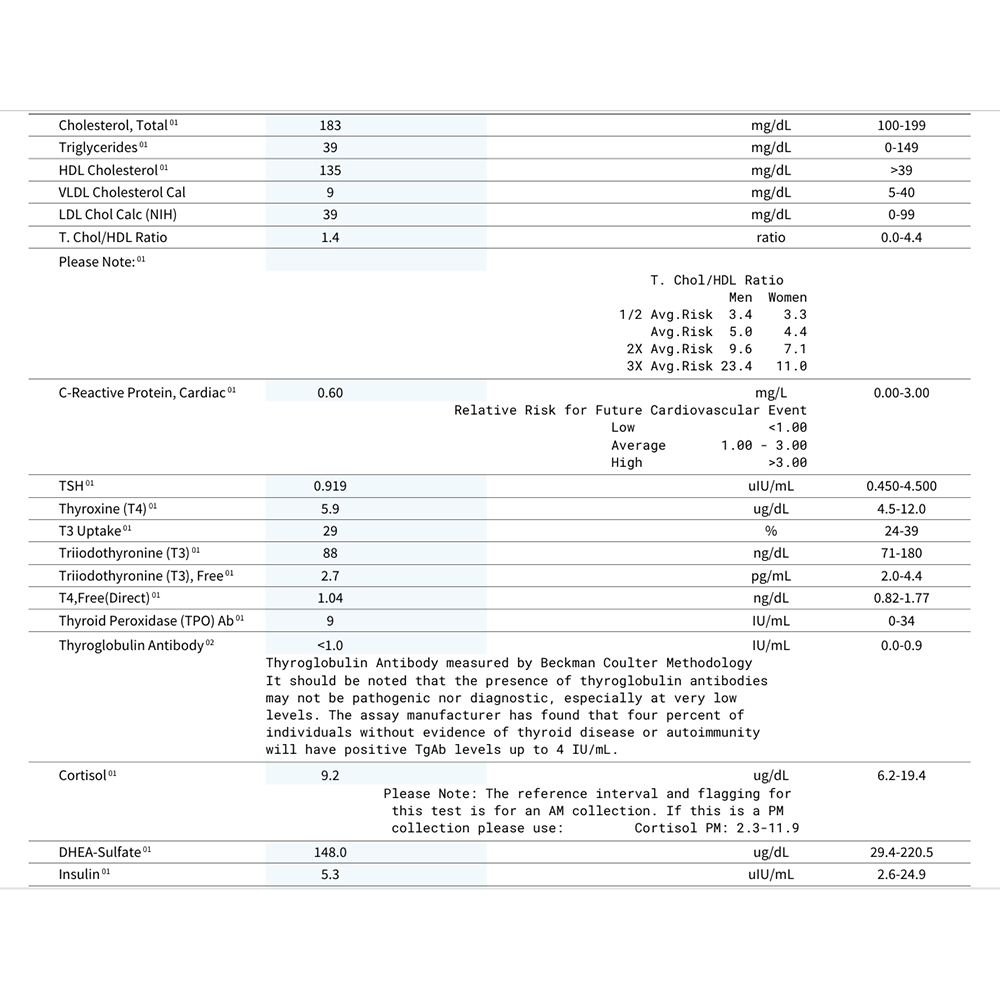
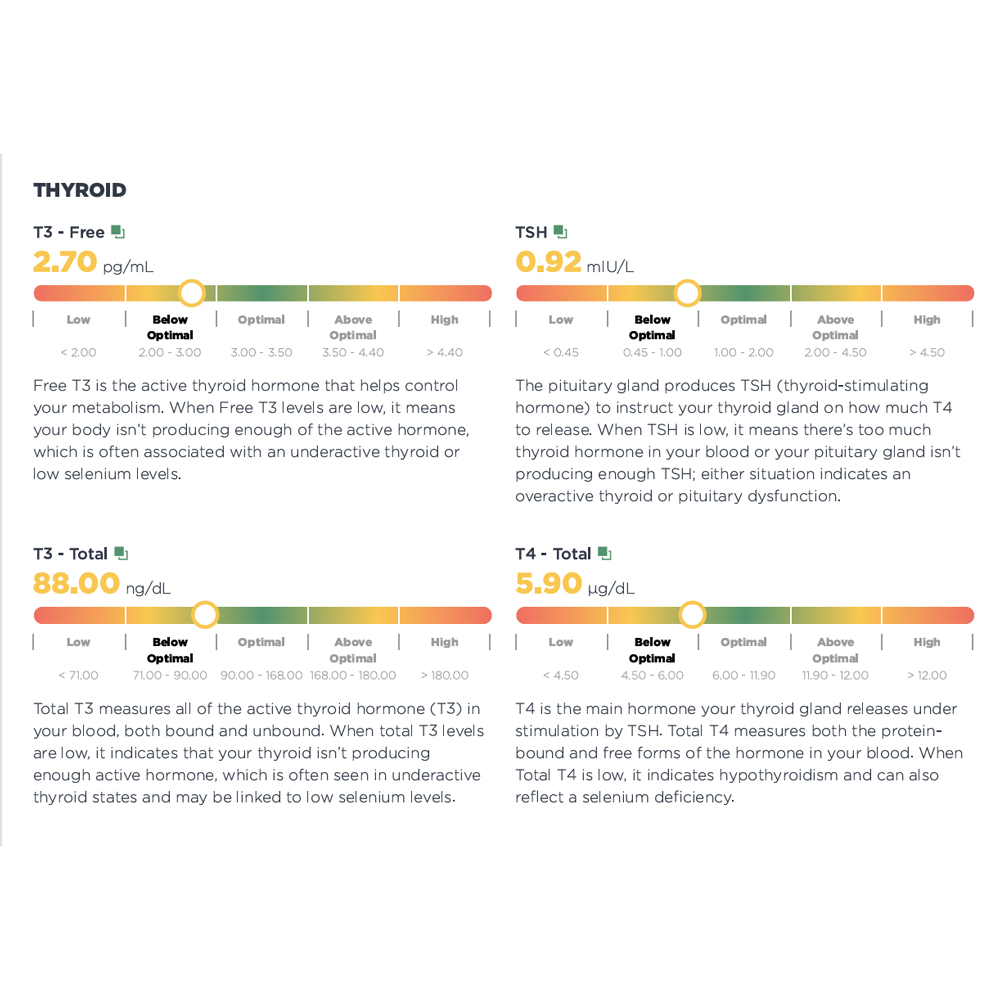
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
A hormone from the pituitary gland that signals the thyroid to produce its hormones (T4 and T3). - T4 (Thyroxine)
A hormone made by the thyroid gland that helps regulate metabolism, energy production, and overall growth. This measures total T4 hormone. - Free T4
The amount of T4 hormone not bound to proteins in the blood. Free T4 is immediately available for use by the cells of your body. - T3 (Triiodothyronine)
A more active thyroid hormone than T4 that plays a key role in controlling metabolism, energy production, growth of tissues and body temperature. - Free T3
The amount of T3 hormone not bound to proteins. Free T3 is immediately available for use by the cells of your body. - T3 Uptake
T3 uptake does not directly measure the uptake of T3 by cells but instead evaluates the extent to which thyroid-binding proteins in the bloodstream are saturated with thyroid hormones. Influenced by inflammation, pregnancy, HRT, oral contraceptives, stress, liver disease, and other factors. - TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase) Antibody
An antibody targeting thyroid peroxidase, an enzyme required to make thyroid hormones. Indicates autoimmune thyroid disease such as Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease. - Thyroglobulin Antibody
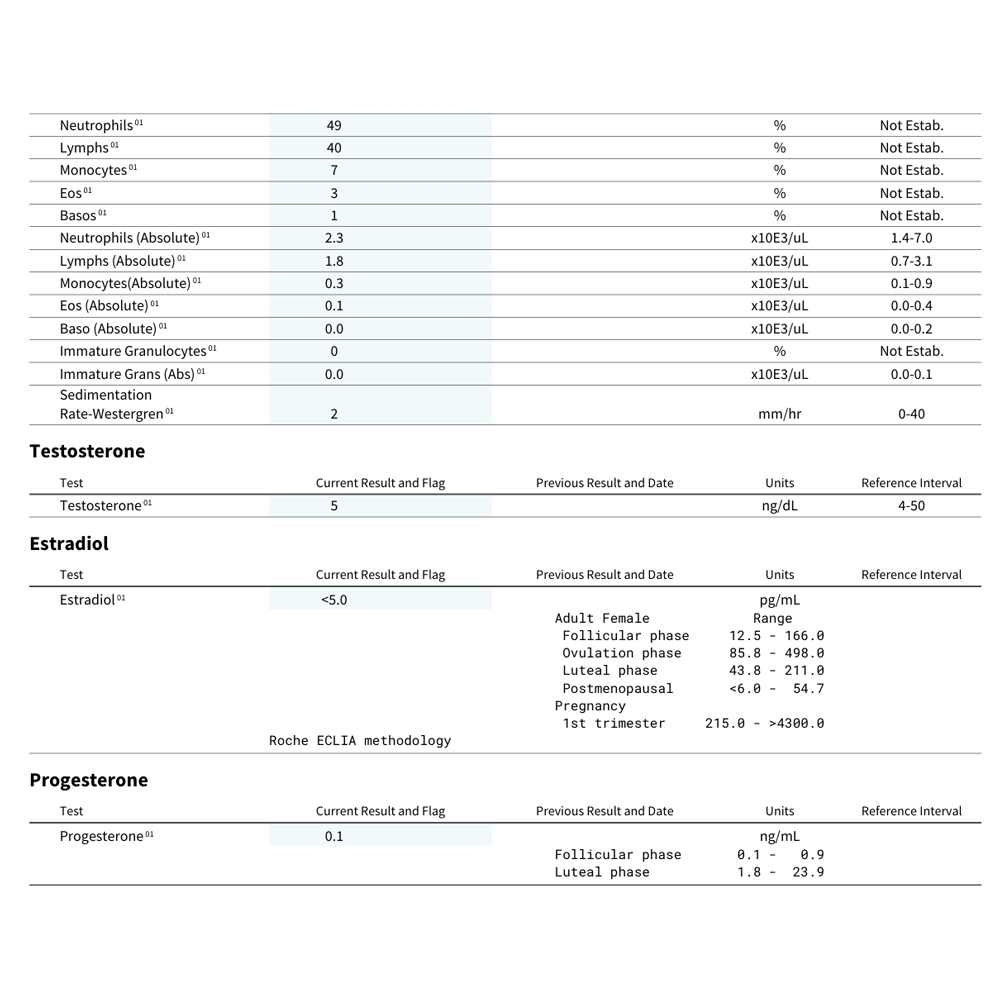
An antibody against thyroglobulin, used to make thyroid hormones. Its presence suggests autoimmune thyroid conditions. - Estradiol (female testing only)
The primary estrogen of reproductive years; important for bone, brain, cardiovascular health, metabolism, and emotional wellbeing. - Progesterone (female testing only)
Influences mood, energy, thyroid function, sleep quality, and emotional wellbeing. - Testosterone (female and male testing)
Essential for bone, muscle health, metabolism, libido, sexual function, and emotional wellbeing. - Free Testosterone (male testing only)
Measures available testosterone; can identify androgen deficiency even when total testosterone is normal. - C-Reactive Protein (high sensitivity)
A sensitive marker of inflammation. - Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Measures how quickly red blood cells settle; higher rates indicate inflammation. - White Blood Cells (WBC)
Immune cells that fight infections; abnormal levels may indicate infections or immune disorders. - Red Blood Cells (RBC)
Carry oxygen to cells; abnormalities can cause anemia and poor cellular metabolism. - Hemoglobin
Protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen for energy and metabolism. - Hematocrit
Percentage of blood made of red blood cells; used to assess anemia and blood disorders. - Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
Determines red blood cell size; small cells suggest iron deficiency, large cells suggest B12 or folate deficiency. - Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
Average amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell. - Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
Concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. - RDW (Red Blood Cell Distribution Width)
Variation in red blood cell size; elevated levels indicate deficiencies, blood loss, or blood disorders. - Platelets
Required for blood clotting; abnormalities may indicate blood disorders. - Neutrophils
Immune cells that fight bacterial and fungal infections. - Lymphocytes
Produce antibodies; elevated levels often indicate viral infections or autoimmune activity. - Monocytes
Remove dead cells and fight infection. - Eosinophils
Fight parasites and mediate allergic reactions. - Basophils
Protect against allergens and infections. - Neutrophils (Absolute)
Total neutrophil count to assess infection risk and inflammation. - Lymphocytes (Absolute)
Total lymphocyte count to assess immune function. - Monocytes (Absolute)
Total monocyte count for immune activity and inflammation. - Eosinophils (Absolute)
Used to evaluate allergies and parasitic infections. - Basophils (Absolute)
Helps identify blood and immune disorders. - Immature Granulocytes
Elevated levels may indicate infections, allergies, or bone marrow disorders. - Immature Granulocytes (Absolute)
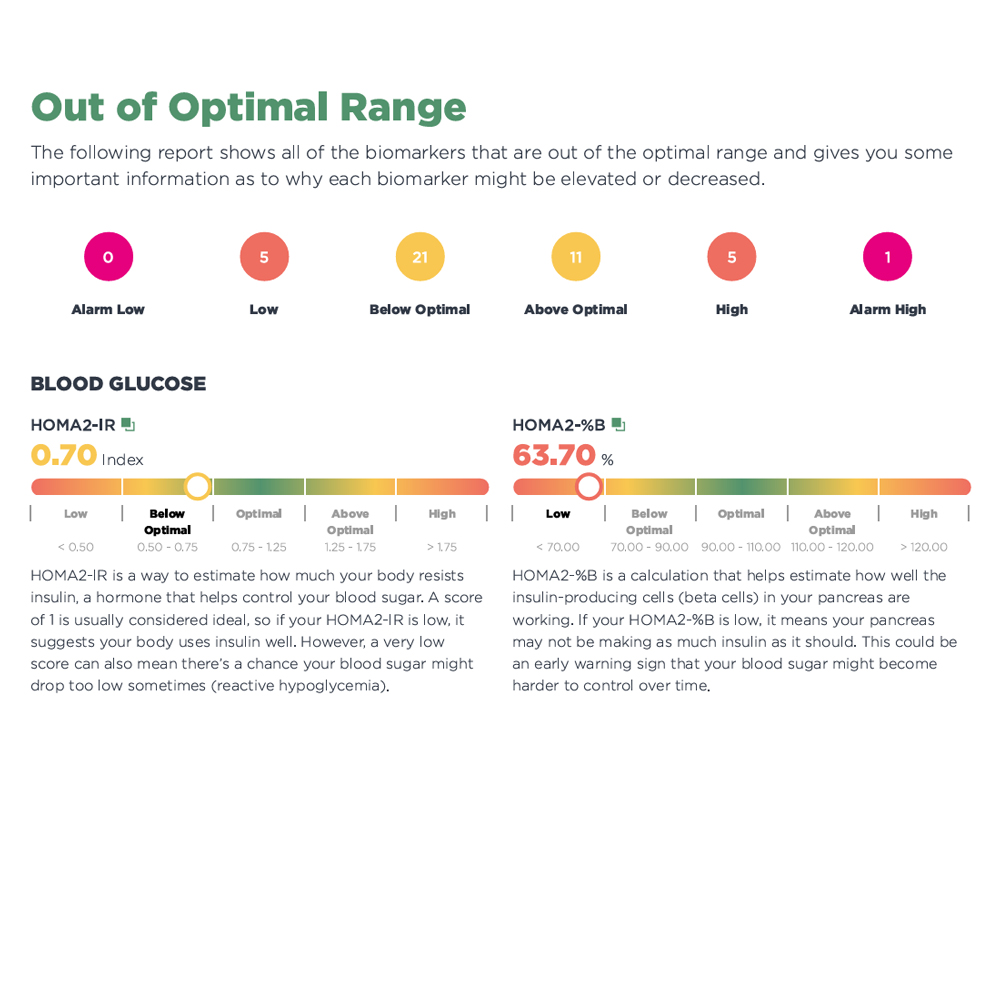
Number of immature granulocytes in the blood. - Insulin (fasting)
Assesses insulin resistance, prediabetes, and diabetes. - Serum Iron
Measures iron in the blood. - TIBC (Total Iron-Binding Capacity)
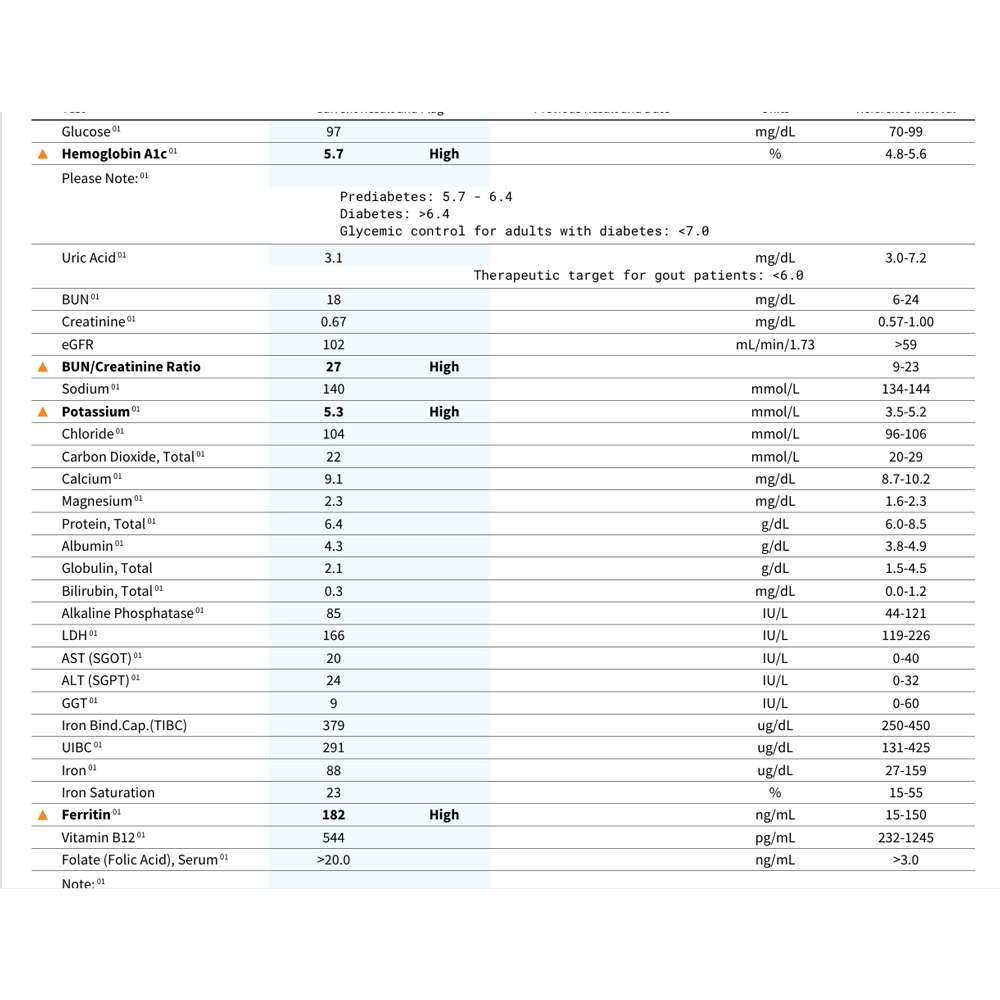
Measures the capacity of blood proteins to carry iron. - Ferritin
Iron storage protein; low levels indicate deficiency, high levels may indicate inflammation. - Cortisol
Stress hormone involved in metabolism, blood sugar regulation, and inflammation. - DHEA-Sulfate
Androgen produced by adrenal glands; elevated in insulin resistance and PCOS. - Magnesium
Supports nerves, muscles, bones, thyroid, and metabolism. - Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
Sensitive liver and gallbladder enzyme; elevated with inflammation or liver issues. - Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
Found in liver, bone, and intestines; abnormalities indicate inflammation or deficiency. - AST (SGOT)
Enzyme in liver, muscle, and organs; elevated with tissue damage or low B vitamins. - ALT (SGPT)
Liver enzyme elevated in inflammation, fatty liver, and injury. - Vitamin D
Essential for bones, calcium absorption, and immune function. - Vitamin B12
Needed for nerves, metabolism, DNA, and red blood cells; absorption impacted by stomach acid. - Vitamin B9 / Folate
Needed for cell growth and metabolism; deficiency causes anemia. - Total Cholesterol
Total cholesterol including LDL, HDL, and VLDL. - Triglycerides
Blood fats associated with diet, blood sugar, and insulin resistance. - HDL Cholesterol
“Good” cholesterol protective for heart health. - VLDL Cholesterol
“Bad” cholesterol carrying triglycerides. - LDL Cholesterol
“Bad” cholesterol linked to heart disease. - Total Cholesterol / HDL Ratio
Lower values reflect lower cardiovascular risk. - Uric Acid
Waste product; high levels linked to gout, kidney issues, and inflammation. - Hemoglobin A1c
Reflects 90-day average blood sugar; used to diagnose diabetes. - Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
Enzyme found throughout the body; elevated with tissue damage or inflammation. - Glucose
Main blood sugar used to evaluate metabolic health. - Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Waste product from protein metabolism; used to assess kidney function. - Creatinine
Waste product from muscle activity; measures kidney filtration. - Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR)
Estimates kidney filtration efficiency. - BUN/Creatinine Ratio
Helps detect kidney problems. - Sodium
Electrolyte for nerve, muscle, and fluid balance. - Potassium
Essential electrolyte for cells and heart function. - Chloride
Works with sodium for fluid balance and digestion; affected by stress and stomach acid levels. - Calcium
Needed for bones, nerves, and muscles; elevated with thyroid/parathyroid issues. - Carbon Dioxide (Total)
Waste product of metabolism. - Protein (Total)
Total blood proteins, including albumin and globulins. - Albumin
Liver-produced protein essential for transport and fluid balance. - Globulin (Total)
Group of proteins essential for immunity and clotting. - A/G Ratio
Compares albumin and globulin to assess liver, kidney, and nutritional status. - Bilirubin (Total)
Byproduct of red blood cell breakdown; abnormalities indicate liver or bile duct issues.